Ansible and Mondoo
Mondoo works seamlessly with configuration management tools in the DevOps ecosystem. For businesses already using Ansible to automate their environments, there are two primary ways to use Mondoo and Ansible together:
-
Continuously assess host configuration: Use Ansible to:
-
Install and configure cnspec on supported Linux and Windows hosts
-
Register hosts with Mondoo Platform
-
Configure hosts to continuously scan with Mondoo policies and report results to Mondoo Platform
-
-
Scan Ansible inventories on demand: Perform on-demand scans of Ansible inventories without installing cnspec as a service on the host.
Hosts from your Ansible inventory authenticate with your Mondoo Platform account so that cnspec can retrieve policies you've enabled. cnspec sends scan results from the host to Mondoo Platform, where you can see asset scores and reports.
If you deploy cnspec to machines that can't download and install updates (because they're air-gapped or don't give cnspec write access), you must deploy cnspec providers. To learn more, read Manage cnspec Providers.
Requirements
-
In your Mondoo Platform account, enable all the policies you want to run against your Ansible inventory. To learn how to enable policies, read Manage Policies.
-
You must have root or administrator access for each host in the Ansible inventory you want to scan.
-
You must have Ansible installed on your workstation. For installation instructions, read the Ansible documentation.
-
All hosts in your inventory must allow outbound traffic on port 443 (HTTPS) to Mondoo Platform at
https://us.api.mondoo.com:443(IP address34.98.71.94) to send results to your account.
Run continuous configuration assessments with Mondoo and Ansible
Use Ansible to install and configure cnspec on supported Linux and Windows hosts so that Mondoo runs continuously as a service.
Mondoo maintains and publishes an official Mondoo/cnspec role, which is available on Ansible Galaxy. The code for the role is open source and available in our GitHub repo.
Mondoo's Ansible role lets you:
-
Install cnspec on supported Linux and Windows hosts
-
Register host on Mondoo Platform
-
Configure cnspec to run as a service at system startup
-
Run continuous security assessments of the host
Once configured, cnspec authenticates with Mondoo Platform every 60 minutes, running every enabled policy. It sends results from the scan to Mondoo Platform so you can see the generated scores and reports in the Mondoo Console.
Set up continuous configuration assessments with Mondoo and Ansible
This section covers how to set up continuous configuration assessments on Linux and Windows hosts with Ansible. After completing this section, you will have an Ansible inventory running cnspec as a service, registered with your Mondoo Platform account, running policy scans, and reporting the findings to Mondoo Platform.
Step 1: Generate a registration token
The Mondoo Ansible role provides a registration_token variable to specify a Mondoo registration token to use to register the client with Mondoo Platform.
-
In the Mondoo Console side navigation bar, under INTEGRATIONS, select Add New Integration.
-
Select Workstation.
By default, tokens expire every 600 seconds. You can extend expiration time by selecting Token Options and setting the expiration time (max: 86400 seconds).
- Copy the registration token to the clipboard.
Step 2: Install the Mondoo role and create a playbook
Install the Mondoo Ansible role from Ansible Galaxy on your local workstation and create an Ansible playbook to call that role on your inventory:
-
Download the Ansible Mondoo role to your workstation:
Download Mondoo role on your workstationansible-galaxy install mondoo.client -
Create a
playbook.yamlfile to run the Ansible Mondoo role on your inventory of hosts. You must update theregistration_tokenvalue with your registration token from Step 1: Generate a registration token above. This example has both Linux and Windows hosts. If you're only using one of these platforms, remove the unneeded section:Example playbook.yml---
- hosts: mondoo_linux_clients
become: yes
roles:
- role: mondoo.client
vars:
registration_token: "PASTE MONDOO REGISTRATION TOKEN"
- hosts: mondoo_windows_clients
roles:
- role: mondoo.client
vars:
registration_token: "PASTE MONDOO REGISTRATION TOKEN"
force_registration: false -
Save the
playbook.yamlfile.
Step 3: Run Ansible
You should already have a hosts.ini file with your Ansible inventory. This is an example hosts.ini with both Linux and Windows hosts:
# Linux Hosts
[mondoo_linux_clients]
3.92.154.110 ansible_user=admin
3.95.154.111 ansible_user=ec2-user
3.82.22.136 ansible_user=ec2-user
54.211.122.215 ansible_user=ec2-user
54.209.155.66 ansible_user=ubuntu
54.146.154.182 ansible_user=ubuntu
# Windows Hosts
[mondoo_windows_clients]
# Windows Hosts WinRM
3.85.201.162 ansible_port=5986 ansible_connection=winrm ansible_user=Administrator ansible_password=changeme ansible_shell_type=powershell ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
54.66.89.204 ansible_port=5986 ansible_connection=winrm ansible_user=Administrator ansible_password=changeme ansible_shell_type=powershell ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
# Windows Hosts SSH
3.235.247.76 ansible_port=22 ansible_connection=ssh ansible_user=Administrator ansible_password=changeme ansible_shell_type=cmd
Run Ansible against your inventory:
ansible-playbook -i hosts.ini playbook.yml
Step 4: View scan reports in the Mondoo Console
Once Ansible runs the playbook.yaml against your inventory, you can view the scan results in Mondoo Platform.
-
In the Mondoo Console side navigation bar, under Inventory, select Operating Systems. All your assets should now be reported and have asset scores for the policies executed.
-
To view detailed results and the policies that ran on an asset, select the asset in the list. If you don't see the asset you want, use the search bar to filter assets.
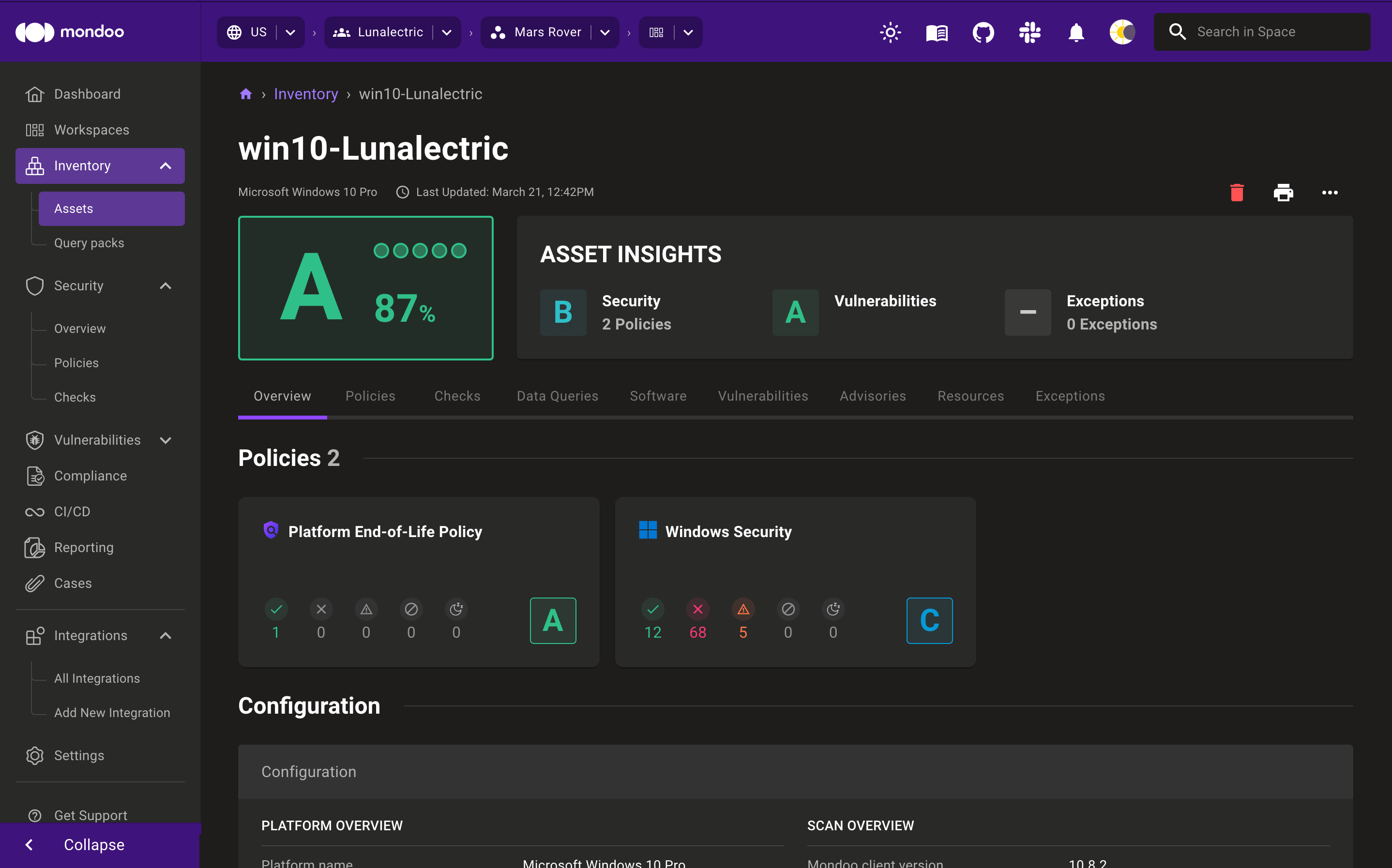
Tabs for policies, checks, and data queries let you dive into greater detail.
To learn more about how Mondoo generates asset scores, read Manage Policies.
cnspec is now running as a service on your Ansible inventory. It continues to scan your assets every 60 minutes and report findings back to your account.
Scan Ansible inventories on demand
While you can easily configure Mondoo's cnspec to run as a service to continuously scan your infrastructure, there may be times when you just want to scan an Ansible inventory without having to install and configure cnspec on your infrastructure.
Mondoo supports on-demand scanning of an Ansible inventory in two ways:
-
Parse the output of the
ansible-inventorycommand and scan with Mondoo. -
Create an Ansible task that uses cnspec to scan your infrastructure.
With both of these approaches, your assets:
-
Authenticate with your Mondoo Platform account using the cnspec configuration on your local workstation
-
Run any policies enabled in that space
-
Return the results to Mondoo Platform so you can view reports and asset scores for all assets in the Mondoo Console.
Because on-demand scans of Ansible inventories run serially, we don't recommend them for large inventories. If you want to run on-demand scans that execute in parallel, please reach out to us in the Mondoo Community Slack channel.
Scan the output of the ansible-inventory command
Step 1: Set up or validate your Ansible inventory
An Ansible inventory is a list of hosts that is mostly stored in the two common formats ini and yaml. These examples illustrate their structure. The ini format allows grouping and easy configuration of additional properties.
[workers]
34.243.41.251 ansible_user=ec2-user
instance1 ansible_host=18.203.250.158 ansible_user=ubuntu
The same structure in yaml:
all:
children:
ungrouped: {}
workers:
hosts:
34.243.41.251:
ansible_user: ec2-user
instance1:
ansible_host: 18.203.250.158
ansible_user: ubuntu
You can validate connectivity with the Ansible inventory by running this command:
ansible all -i hosts.ini -m ping
Example output
instance1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
34.243.41.251 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Step 2: Scan the Ansible inventory
The method for scanning an Ansible inventory depends on whether your shell supports |.
Option A: Pipe the Ansible inventory to cnspec scan
The first option if you are using a shell such as bash or zsh that supports | redirects is to pipe the output of the ansible-inventory -i hosts.ini --list command to cnspec scan --inventory-format-ansible. If the inventory file is
ansible-inventory -i hosts.ini --list | cnspec scan --inventory-file - --inventory-format-ansible
Option B: Scan Ansible inventory hosts.json
If your shell does not support pipes, you can generate a hosts.json from the ansible-inventory command and then pass that file to cnspec scan using the --inventory-file flag.
ansible-inventory -i hosts.ini --list > hosts.json
cnspec scan --inventory-file hosts.json --inventory-format-ansible
Generate a hosts.json file from the ansible-inventory command and then pass that file to cnspec scan using the --inventory-file flag.
ansible-inventory -i hosts.ini --list > hosts.json
cnspec scan --inventory-file hosts.json --inventory-format-ansible
Both cnspec and the Mondoo Console show results from each policy that runs against your assets.
Show or hide example CLI scan output.
Checks:
✓ Pass: Ensure no known platform advisories exist
✓ Pass: Ensure talk server is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure SNMP server is stopped and not enabled
. Skipped: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/passwd- are set
✓ Pass: Ensure no duplicate UIDs exist
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure rsyslog is installed
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure broadcast ICMP requests are ignored
✓ Pass: Ensure rsync service is stopped and not enabled
. Skipped: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/gshadow- are set
. Skipped: Ensure journald is configured to send logs to rsyslog
✓ Pass: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/group are set
✓ Pass: Ensure LDAP server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure events that modify the system's Mandatory Access Controls are collected
✓ Pass: Ensure Samba is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure TCP SYN Cookies is enabled
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure source routed packets are not accepted
✓ Pass: Ensure Avahi server is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure DHCP server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure session initiation information is collected
✓ Pass: Ensure default group for the root account is GID 0
✓ Pass: Ensure HTTP servers are stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure login and logout events are collected
✓ Pass: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/gshadow are set
. Skipped: Ensure journald is configured to write logfiles to persistent disk
✓ Pass: Platform is not end-of-life
✓ Pass: Ensure UID_MIN is set to 1000
. Skipped: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/group- are set
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure auditd is installed
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure events that modify user/group information are collected
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure changes to system administration scope (sudoers) is collected
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment (AIDE) is installed
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure IP forwarding is disabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure audit log storage size is configured
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure packet redirect sending is disabled
✓ Pass: Ensure tftp server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure ICMP redirects are not accepted
✓ Pass: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/passwd are set
✓ Pass: Ensure IMAP and POP3 server is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure no duplicate user names exist
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure system administrator actions (sudolog) are collected
✓ Pass: Ensure all GIDs in /etc/passwd exist in /etc/group
✓ Pass: Ensure telnet server is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure FTP server is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure rsh server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure kernel module loading and unloading is collected
✓ Pass: Ensure no duplicate group names exist
✓ Pass: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/shadow are set
✓ Pass: Ensure system accounts are non-login
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure unsuccessful unauthorized file access attempts are collected
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure address space layout randomization (ASLR) is enabled
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure rsyslog Service is enabled
. Skipped: Ensure journald is configured to compress large log files
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure events that modify date and time information are collected
✓ Pass: Ensure NIS server is stopped and not enabled
. Skipped: Ensure secure permissions on /etc/shadow- are set
✓ Pass: Ensure root group is empty
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure the audit configuration is immutable
✓ Pass: Ensure no duplicate GIDs exist
✓ Pass: Ensure X Window System is not installed
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure events that modify the system's network environment are collected
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure discretionary access control permission modification events are collected
✓ Pass: Ensure no known platform CVEs exist
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure access to the su command is restricted
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure system is disabled when audit logs are full
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure IPv6 router advertisements are not accepted
! Error: Ensure mail transfer agent is configured for local-only mode
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure secure ICMP redirects are not accepted
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure file deletion events by users are collected
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure Reverse Path Filtering is enabled
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure core dumps are restricted
! Error: Ensure filesystem integrity is regularly checked
! Error: Ensure sudo logging is enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure prelink is disabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure secure permissions on all log files are set
✓ Pass: Ensure CUPS is stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure HTTP Proxy server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure suspicious packets are logged
✓ Pass: Ensure each user is a member of a group
✓ Pass: Ensure NFS and RPC are stopped and not enabled
✓ Pass: Ensure DNS server is stopped and not enabled
✕ Fail: F 0 Ensure bogus ICMP responses are ignored
✓ Pass: Ensure shadow group is empty
✕ Fail: C 40 Ensure rsyslog default file permissions configured
. Skipped: Ensure auditing for processes that start prior to auditd is enabled
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure auditd service is enabled
✕ Fail: Ensure the platform is not End-of-Life
✕ Fail: Ensure audit logs are not automatically deleted
✕ Fail: D 20 Ensure successful file system mounts are collected
Vulnerabilities:
■ No advisories found (passed)
Overall CVSS score: 0.0
Scanned 1 assets
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
C mysystem.internal.dmz
For detailed output, run this scan with "-o full".
See more scan results and asset relationships on the Mondoo Console: https://console.mondoo.com/space/inventory/12ejfpX1SbxfrNf6bq8f8gCCgMb?spaceId=ansible-hosts
Step 3: View scan reports in the Mondoo Console
Once Ansible completes, cnspec sends scan results to Mondoo Platform so you can see the generated scores and reports in the Mondoo Console..
To view the reports in the Mondoo Console:
-
In the Mondoo Console side navigation bar, under Inventory, select Operating Systems. All your assets should now be reported and have asset scores for the policies executed.
-
To view detailed results and the policies that ran on an asset, select the asset in the list. If you don't see the asset you want, use the search bar to filter assets.

Tabs for policies, checks, and data queries let you dive into greater detail.
We rely on the ansible-inventory command to support various inventory formats and re-use dynamic inventory. This command outputs a standardized format independently if a ini or yaml inventory is used.
Currently Mondoo does not support group patterns. If you need additional support, please contact us.
Scan on demand using an Ansible task
You can use the cnspec scan command in an Ansible task. Mondoo uses the ssh-agent so you do not need to set up additional credentials configuration.
Step 1: Set up or validate your Ansible inventory
An Ansible inventory is a list of hosts that is mostly stored in the two common formats ini and yaml. These examples illustrate their structure. The ini format allows grouping and easy configuration of additional properties.
[workers]
34.243.41.251 ansible_user=ec2-user
instance1 ansible_host=18.203.250.158 ansible_user=ubuntu
The same structure in yaml:
all:
children:
ungrouped: {}
workers:
hosts:
34.243.41.251:
ansible_user: ec2-user
instance1:
ansible_host: 18.203.250.158
ansible_user: ubuntu
You can validate connectivity with the Ansible inventory by running this command:
ansible all -i hosts.ini -m ping
Example output
instance1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
34.243.41.251 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Step 2: Set up playbook.yaml to run cnspec scan
Create a playbook to run a cnspec scan against your inventory. This is an example playbook.yaml used to execute the scan locally with a playbook against Linux hosts:
---
- hosts: all
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: add key to ssh-agent
local_action: ansible.builtin.command ssh-agent
run_once: true
- name: add key to ssh-agent
# activate rsa key if that is used
# local_action: command ssh-agent ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
local_action: ansible.builtin.command ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
run_once: true
- name: run cnspec scan for target destination
local_action: ansible.builtin.command cnspec scan --insecure --score-threshold 0 ssh {{ ansible_user }}@{{ inventory_hostname }}
Be sure to save the file.
Step 3: Run Ansible
Run the playbook with this command:
ansible-playbook -i hosts.ini playbook.yml
Step 4: View scan reports in the Mondoo Console
Once Ansible completes, scan results are sent to Mondoo Platform so you can view asset scores and reports for all assets scanned in the Mondoo Console.
To view the reports in the Mondoo Console:
-
In the Mondoo Console side navigation bar, under Inventory, select Operating Systems. All your assets should now be reported and have asset scores for the policies executed.
-
To view detailed results and the policies that ran on an asset, select the asset in the list. If you don't see the asset you want, use the search bar to filter assets.

Tabs for policies, checks, and data queries let you dive into greater detail.
To learn more about how Mondoo scores assets, read Score Policies.