Policy Authoring Guide | Score Policies
Now that you've explored the very basic elements of a policy and a policy bundle, you can decide how to calculate asset security based on this policy.
Each scanned target receives a risk score that summarizes how well it compares to the checks in the policy. Risk scores are based on numeric scores between 0 and 100. These are the ranges for Mondoo risk scores:
| From… | To… | Risk score | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 100 | CRITICAL | Presents extreme risk to your organization |
| 70 | 89 | HIGH | Presents significant risk to your organization |
| 40 | 69 | MEDIUM | Presents moderate risk to your organization |
| 1 | 39 | LOW | Presents little risk to your organization |
| 0 | 0 | NONE | Presents no risk to your organization |
The score is based on the number of checks that return a true value (pass) compared to how many return a false value (fail).
When assessing the overall security of an asset, some checks may be more important than others. For example, suppose a strong cipher is more important to your organization than SSH using port 22. You can use the impact attribute to give more importance to one check and less importance to another check. The Ensure the port is set to 22 check has an impact of 90 (on line 18) and the Prevent weaker CBC ciphers from being used check has an impact of 80 (on line 23):
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: highest impact
authors:
- name: Lunalectric
email: security@lunalectric.com
docs:
desc: |-
Descriptive documentation about this policy
groups:
- title: group1
checks:
- uid: sshd-01
title: Ensure the port is set to 22
mql: sshd.config.params["Port"] == 22
impact: 90
- uid: sshd-02
title: Prevent weaker CBC ciphers from being used
mql: sshd.config.ciphers.none( /cbc/ )
impact: 80
queries:
- uid: sshd-d-1
title: Gather SSH config params
mql: sshd.config.params
How Mondoo uses these values to calculate an asset's score depends on the scoring_system setting (line 5). You can choose from these scoring systems:
-
Average
-
Weighted (average)
-
Banded (recommended)
-
Decayed
-
Highest (failed) impact
Average scoring system
The average scoring system considers impact before averaging check scores. Failed checks with higher impact lower an overall score more than checks with lower impact. This is how the average scoring system calculates the overall score:
-
If a check passes (returns
true), the asset receives a 0 for that check. -
If a check fails (returns
false), the asset receives the impact value for that check. For example, if an asset fails a check with an impact of 90, it receives a 90 for that check.
Our simple example query above contains:
-
A port check (sshd-01) with an impact of 90
-
A cipher check (sshd-02) with an impact of 80
These are the possible asset scores on this policy:
| Port check (impact 90) | Cipher check (impact 80) | Overall score |
|---|---|---|
| Pass (0) | Pass (0) | (0 + 0) / 2 = 0 or None |
| Pass (0) | Fail (80) | (0 + 80) / 2 = 40 or Medium |
| Fail (90) | Pass (0) | (90 + 0) / 2 = 45 or Medium |
| Fail (90) | Fail (80) | (90 + 80) / 2 = 85 or High |
The average scoring system can produce overly positive results for assets that fail checks with very high impact scores.
To use the average scoring system, set the scoring system value to average:
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: average
Weighted average scoring system
The weighted average scoring system is just like the average scoring system except that it also considers another factor when calculating an asset's score: the weight value assigned to a check. This scoring system gives checks with higher weight greater influence over an asset's total score than checks with lower weight.
The weighted average scoring system can produce overly positive results for assets that fail checks with very high impact scores.
To use the weighted average scoring system, set the scoring system value to weighted:
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: weighted
Banded scoring system (recommended)
The banded scoring system groups checks into these bands based on their impact values:
| Band | From... | To... |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | 90 | 100 |
| High | 70 | 89 |
| Medium | 40 | 69 |
| Low | 0 | 39 |
For example, a check with an impact value of 90 is in the critical band; it has critical impact. A check with an impact value of 10 is in the low band; it has low impact.
The banded scoring system calculates an asset's score on a policy based on a combination of check results and impact bands.
It also uses impact bands to prevent overly-positive asset scores: If an asset fails one or more critical checks, the asset's maximum possible overall score is 50. For example, suppose you scan an asset using a policy with 99 checks with an impact of 70 (high band) and one check in the with an impact of 90 (critical band). If the asset fails the single critical check, its overall score can't be higher than a 50. Even if it passes all the high band checks, it still gets a 50 because of the single critical failure.
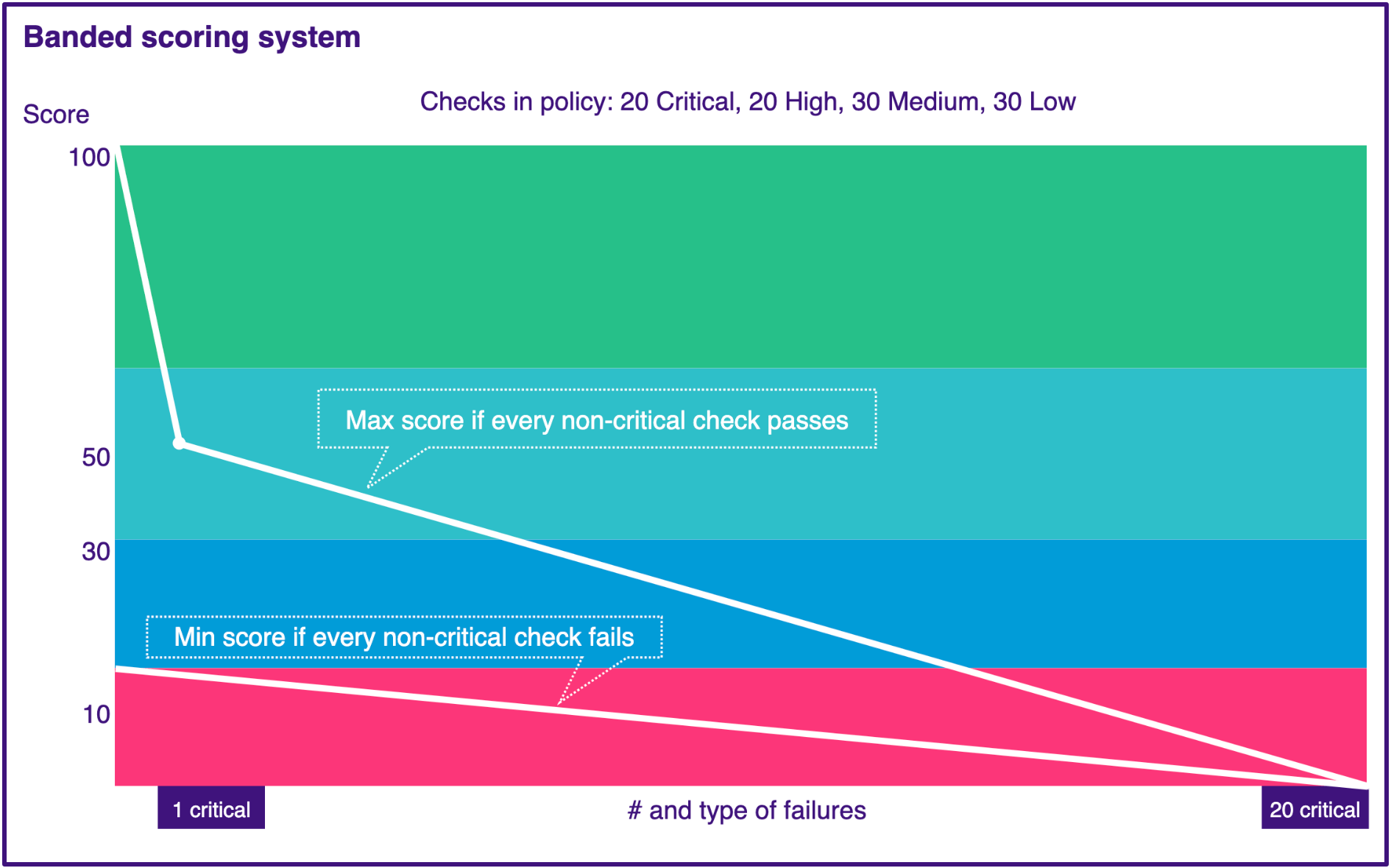
In addition, the banded scoring system:
-
Ensures that the score quickly goes down as the number of critical findings increase
-
Takes into account other scoring failures (like high and medium)
-
Guarantees a minimum score when an asset has no critical or high failures
For these reasons, Mondoo recommends the banded scoring system to most of our customers.
To use the banded scoring system, set the scoring system value to banded:
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: banded
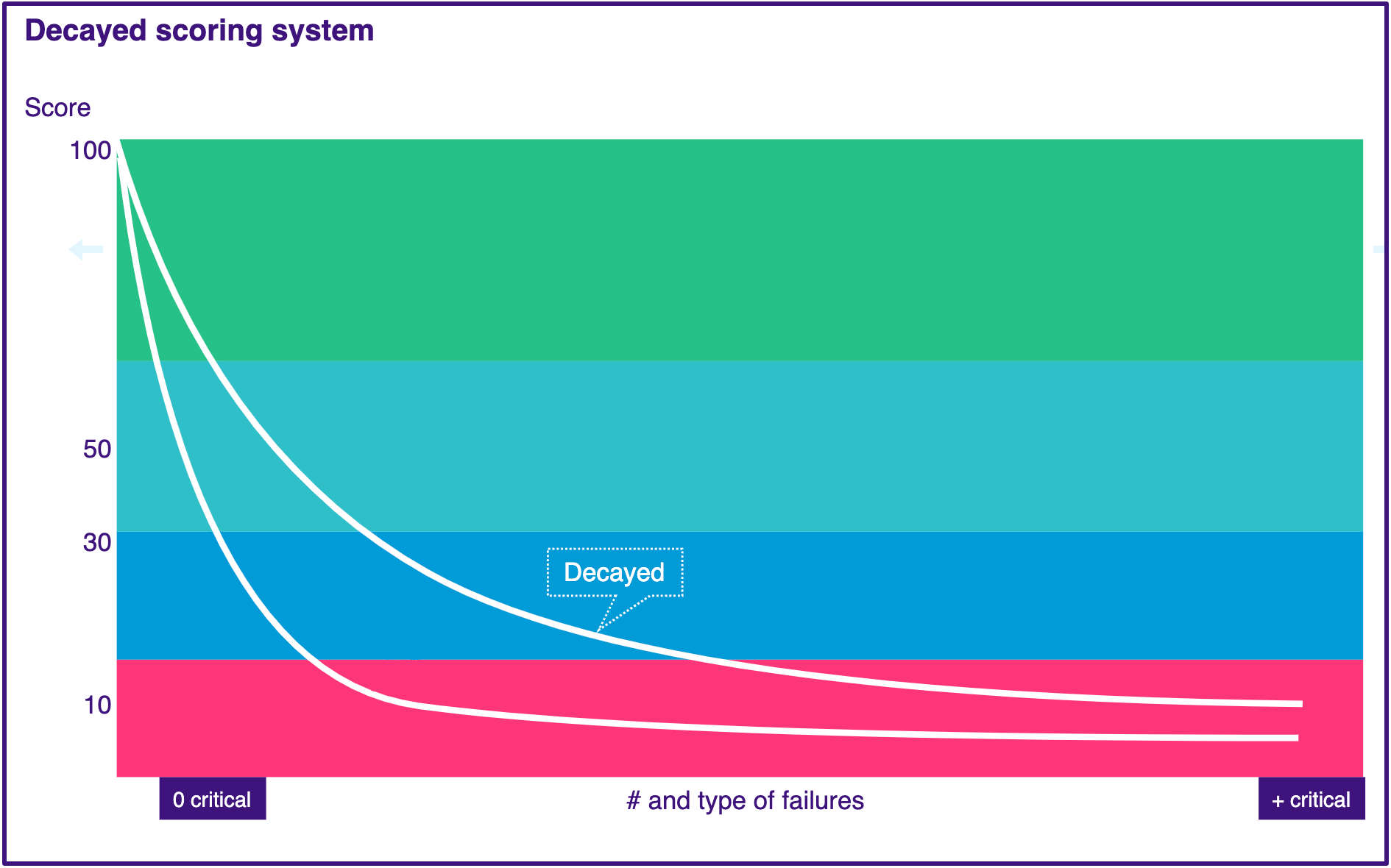
Decayed scoring system
Like the average and banded scoring systems, the decayed scoring system calculates an asset's score based on the impact of the checks that pass and fail. What's unique is that it scores assets on a curve. It uses exponential decay: As checks fail, this system decreases the score of the asset at a rate proportional to its current value. The decayed scoring system:
-
Quickly reduces scores as critical findings are added
-
Doesn't sink scores to zero too quickly as more checks fail
To use the decayed scoring system, set the scoring system value to decayed:
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: decayed
Highest (failed) impact scoring system
The highest impact scoring system only considers the highest-impact check in the policy. It relies on the same method of subtraction as the average scoring system: It subtracts the impact value from 100 if a check fails. It then takes the score of the highest-impact failed check and makes that the overall score.
To use the highest impact scoring system, set the scoring system value to highest impact:
policies:
- uid: simple-example1
name: Simple example policy 1
version: "1.0.0"
scoring_system: highest impact
Which scoring system is right for you?

Mondoo recommends the banded scoring system for all but the most risk-averse organizations. It produces a score that reflects the risk that critical failures introduce to your infrastructure and also changes as your team makes security fixes.
More risk-averse companies can choose the decayed scoring system. It's more sensitive to all failures, especially to high and critical checks, but tends to grant lower scores than the banded system.
The highest impact scoring system is useful only for the most risk-averse teams who can't tolerate any check failures. On the other end of the spectrum, the average scoring system and weighted average scoring system provide a very positive representation of an asset's security, and at the same time may not motivate teams to improve.
Show or hide detailed examples of policy scores.
To demonstrate how the different scoring systems evaluate an asset and reflect the important security improvements that a team makes, here are example scores for a hypothetical policy. This is a somewhat typical policy containing 100 checks, distributed across all four bands:
-
10 critical-impact checks
-
15 high-impact checks
-
30 medium-impact checks
-
45 low-impact checks
These examples don't include the weighted average scoring policy because its behavior is so similar to the average scoring policy.
When Mondoo first scans the asset based on the example policy, the asset:
-
Fails 5 of 10 critical-impact checks
-
Fails 10 of 15 high-impact checks
-
Fails 2 of 30 medium-impact checks
-
Fails 1 of 45 low-impact checks
These are the scores the different systems calculate for the asset:
| System | Score | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|
| Average | 85 | Low |
| Banded | 11 | High |
| Decayed | 4 | Critical |
| Highest impact | 0 | Critical |
Note that the average scoring system gives the asset an A even though it's failing half the critical-impact checks in the policy. The other scoring system accurately reflect these important failures.
Suppose the team fixes the asset so that it now passes 5 of the high-impact checks. The asset now:
-
Fails 5 of 10 critical-impact checks
-
Fails 5 of 15 high-impact checks
-
Fails 2 of 30 medium-impact checks
-
Fails 1 of 45 low-impact checks
| System | Score | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|
| Average | 89 | Low |
| Banded | 17 | High |
| Decayed | 11 | High |
| Highest impact | 0 | Critical |
The average scoring system continues to report sunny results. The banded scoring system still reflects the high quantity of critical-impact failures. The decayed scoring system reflects the improvement. And the highest impact scoring system doesn't change.
Now suppose the team makes improvements to the asset so that it now passes another high-impact check and 3 more of the critical-impact checks. The asset now:
-
Fails 2 of 10 critical-impact checks
-
Fails 4 of 15 high-impact checks
-
Fails 2 of 30 medium-impact checks
-
Fails 1 of 45 low-impact checks
| System | Score | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|
| Average | 93 | Low |
| Banded | 30 | High |
| Decayed | 25 | High |
| Highest impact | 0 | Critical |
There's no change in the average, decayed, or highest impact scores. The banded scoring system shows improvement with a D.
Finally, the team fixes all but one critical issue. The asset now:
-
Fails 1 of 10 critical-impact checks
-
Fails 4 of 15 high-impact checks
-
Fails 2 of 30 medium-impact checks
-
Fails 1 of 45 low-impact checks
| System | Score | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|
| Average | 94 | Low |
| Banded | 34 | Medium |
| Decayed | 31 | Medium |
| Highest impact | 0 | Critical |
There's still no change in the average or highest impact scores. The banded score also remains a C and the decayed score rises to a C as well.
Summary
Throughout this example:
-
The average scoring system showed an overly optimistic score that didn't change as the team fixed issues.
-
The banded scoring and decayed scoring systems presented accurate assessments and reflected changes as the asset's configuration improved.
-
The highest impact scoring system maintained an F for the asset because it still had at least one critical-impact check failure.
Change a policy's scoring system in a Mondoo space
Mondoo Enterprise users can customize what scoring system a policy uses for assets within a Mondoo space, regardless of the scoring system set in the policy. To learn more, read Change a Policy's Scoring System within a Space.
Scoring and multiple policies
When Mondoo evaluates an asset based on more than one policy, it uses a weighted average to calculate a single asset score. It weights the individual policy scores based on the number of checks in the policies.
For example, suppose Mondoo assesses an asset based on two policies:
-
Policy X contains 100 checks.
-
Policy Y contains 20 checks.
If an asset scores 72 on policy X and scores 50 on policy Y:
-
Multiply policy x score by 100 because the policy contains 100 checks.
72 x 100 = 7200
-
Multiply policy y score by 20 because the policy contains 20 checks.
50 x 20 = 1000
-
Divide the sum of the two policies by the total number of checks in both policies.
(7200 + 1000) / 120 = 68 (B)
Next steps
-
To learn how to write more powerful policies, read Reuse Queries and Checks.
-
If you're ready to create your own policy: To learn how to set up, validate, and store policy bundles, read Manage Policies.